2 Retirement Plans You Must Know in Singapore
Anyone living in Singapore must perform the essential task of retirement planning. Having a plan in place is essential for ensuring financial security during retirement. The reason for this is the ever-growing cost of living and increasing medical care expenses, not to mention the "good problem" of increasing longevity.
What is a retirement plan? To attain its objectives, a retirement plan involves setting aims for post-retirement income and identifying all necessary measures. This financial strategy can assist in preparation for one's retirement years. A retirement plan includes identifying income sources, estimating expenses, implementing a savings program, and managing assets and risks.
Having enough financial resources to sustain the retiree in the retirement years is precisely what retirement planning intends to ensure. For retirement planning, Singapore savings bonds and ETFs are popular investment vehicles among many that employer-sponsored plans often include.
To enjoy your golden years without concerns about running out of money, it is crucial to have retirement plans. In addition, they provide a sense of security and peace of mind for what lies ahead.

From public retirement schemes to private sector options, Singapore offers multiple retirement plan types. This article discusses some of the most popular and important retirement plans to invest in. Considering these plans is important while planning for your financial future. Note that any private plans are extra, and generally, it is seen that SRS is most suitable as a first stop after the mandatory CPF.
The advantages that come with each plan will be examined. Moreover, we will examine their potential to help you achieve your retirement targets. Proper planning and information can ensure a secure and comfortable retirement in Singapore.
Central Provident Fund (CPF)
This is the mandatory retirement plan. Serving as a mandatory social security savings scheme, the Central Provident Fund (CPF) applies to all employees in Singapore. A comprehensive system supplies members with retirement, healthcare, and housing benefits. CPF satisfies your retirement requirements in two ways: (1) A monthly payout is given. (2) You can withdraw from your retirement fund to fulfil any immediate cash needs.
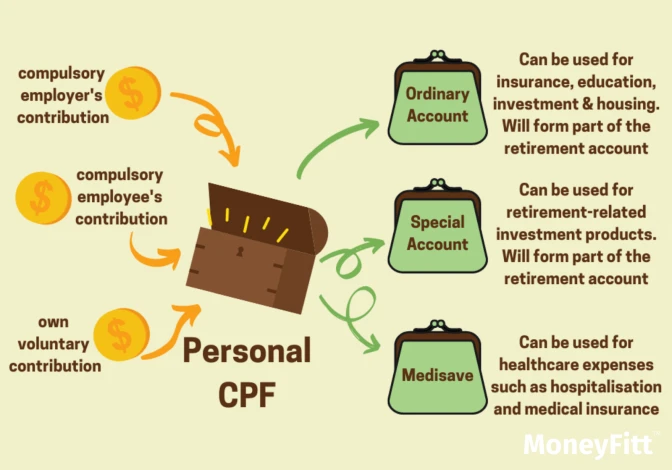
CPF LIFE, a lifelong annuity scheme, is among the crucial retirement benefits CPF provides. The Singapore government guarantees CPF LIFE savings, while members can earn high, risk-free interest of up to 6% annually. This initiative ensures that members will receive periodic payments throughout their lives. They will receive retirement income regardless of their lifespan.
By making cash top-ups into either their own Special Account (SA) or Retirement Account (RA), members can look forward to receiving increased retirement payouts. SA or RA top-ups can be made by those aged 55 or above for their loved ones. At least $60,000 must be in the RA of Singapore citizens or permanent residents born after 1958, six months before turning age 65. Qualifying for payouts is possible under the CPF LIFE scheme. In case of urgent cash needs, CPF members can access, with conditions, withdrawal facilities.
Supplementary Retirement Scheme (SRS)
A voluntary savings plan, the Supplementary Retirement Scheme (SRS), complements the Central Provident Fund (CPF) in Singapore. The SRS forms part of the Singapore government's strategy to cater to the financial requirements of a growing elderly demographic. Saving for old age is made easier with its assistance for Singaporeans. Participating in the SRS is at one's discretion. Individuals can control how they want to invest money in SRS by contributing an amount within the given limit.
SRS contributions qualify for tax relief, while investment returns can be accumulated without taxes (Singapore dividends excluded). Taxation is applicable on just half of the SRS withdrawals upon retirement. Contributions made by Singapore citizens and permanent residents towards their SRS accounts can be at most $15,300 annually. In comparison, the limit for foreign individuals is set at $35,700.

Contributions may be employed to buy diverse investment tools. Recent upgrades have enabled investors to withdraw from their SRS accounts in investment form while raising the contribution ceiling. Opening an SRS account requires Singapore citizenship, permanent residency status or any source of income for foreigners. You can receive tax relief while increasing your savings for retirement with the SRS.
Staggered SRS Withdrawals
Staggered SRS withdrawals involve taking out funds gradually from the Supplementary Retirement Scheme (SRS) account over typically 10 years to minimise tax liabilities while in retirement.
A steady stream of income can be enjoyed by retirees using this method while they can avoid a big tax bill in any one year. The Singapore government introduced a voluntary savings scheme called SRS complements CPF. It aims to help Singaporeans save more for their old age, moreover. Eligibility for tax relief is granted for contributions to SRS, and only 50% of the withdrawals from SRS during retirement are taxable.
Potentially withdrawing tax-free amounts yearly is possible for individuals who optimise their tax benefits. Spreading SRS withdrawals over a period of 10 years can help them achieve this. Upon reaching 63 years old and having $400,000 saved in their SRS account, a retiree could withdraw $40,000 annually from the same.
This example illustrates how the SRS scheme can be advantageous for retirees. Taxation applies to only 50% of the $40,000 in this case. The initial $20,000 of an individual's income is tax-free and exempts the retiree from paying tax for the SRS withdrawal. However, the retiree will be taxed accordingly if the withdrawal exceeds $20,000.
There are penalties for withdrawing early from the SRS account, which is important to note. Subject to a 5% penalty based on the amount withdrawn are withdrawals made before the statutory retirement age. In addition, taxation will apply to the complete withdrawal amount. When making their first contribution, individuals must consider that the statutory retirement age is the prevailing retirement age.
