Singapore's Corporate Tax Rates: A Guide to Low Taxes and Incentives
Tax is not exclusive to the individual!
- Taxes are a financial charge on the taxpayer by a governmental organisation, used to help fund public goods and services such as healthcare, education, infrastructure and defence.
- Corporate tax is a tax on a corporation’s profits and is a flat rate in Singapore.
- Singapore has notoriously low corporate tax rates at 17%. These relatively low tax rates can be further lowered thanks to incentives introduced by IRAS.
Singapore’s Corporate Tax Rates
Singapore's historically attractive tax rates for foreign investors have given it a tax-haven status and contributed to its status as a global financial hub. Corporate tax, which is a tax on an organisation’s profits, sits at a flat rate of 17%. For comparison, the global average is 23%.
In addition, these relatively low tax rates can be further lowered thanks to incentives introduced by IRAS, such as tax exemption, tax incentives, and tax rebates.
Examples
The Tax Exemption Scheme for New Start-Up Companies allows them to benefit from a tax exemption of up to $125,000 on the first $200,000 of chargeable income during their initial three years of business, as demonstrated below:
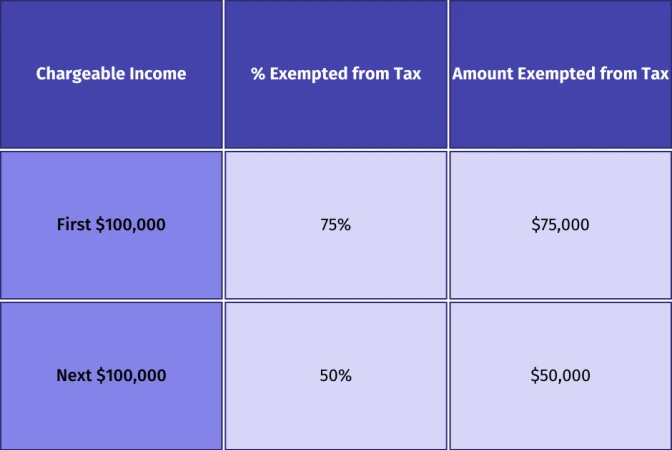
Maximum exemption for each YA = $125,000 ($75,000 + $50,000)
To qualify, companies must be incorporated in Singapore, pay tax in Singapore for that YA, and not have more than 20 shareholders*.

Suppose a company has not previously claimed the Tax Exemption Scheme for New Start-Up Companies. In that case, it can take advantage of the Partial Tax Exemption for companies, allowing them a maximum exemption of $102,500 on the first $200,000 of chargeable income, as demonstrated below:
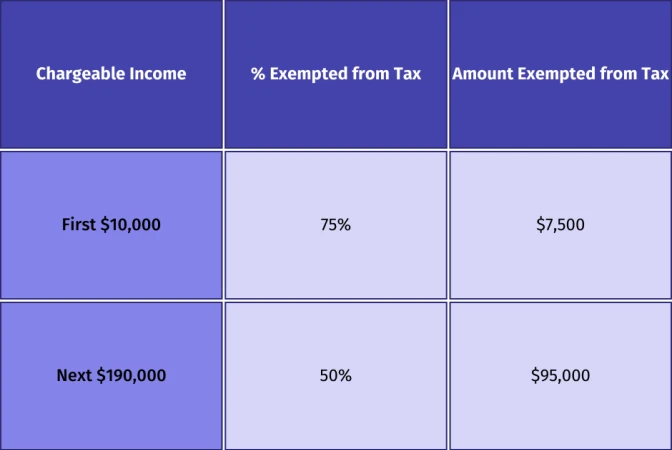
Maximum exemption for each YA = $102,500 ($7,500 + $95,000)
There is also tax exemption for foreign-sourced income, including:
- Foreign-sourced dividend
- Foreign branch profits
- Foreign-sourced service income
Industries With Specific Tax Incentives
- Financial services
- Banks
- Legal firms
- Fund Management Industry
- Global Trading Companies
- Processing Services
- Shipping & Maritime Industry
- Event Organisers
- eCommerce Industry
- Ventures (accepted ones only)
- R&D, Product Development and Innovation
- Insurance companies
When Are Corporate Taxes Due?
Taxes must be filed by November 30th of the assessment year for income gained in the preceding tax year (tax year ends 31st December).
Additional Types
Property Tax (Commercial)
A tax levied on property owners based on their properties’ expected rental value. In Singapore, it is a flat rate (10%) of the annual property value. Property tax forms roughly 8% of total tax revenue.
Stamp Duty
Levied on commercial and legal documents associated with stocks & shares, immovable properties, mortgages and share transfer documents. A common example of stamp duty being applied is when a property is purchased, sold, or leased. The tax is progressive, getting higher as the property value increases. Rates range from 1-6% for residential property, or 1-5% for non-residential property. The tax forms roughly 11% of total tax revenue.

CORPORATE TAX RATES. COMPLETED. ✅
Sources:
- https://www.guidemesingapore.com/business-guides/taxation-and-accounting/corporate-tax/industry-specific-tax-incentives-in-singapore#Accordion-Item-Element-14
- https://www.investopedia.com/ask/answers/060716/why-singapore-considered-tax-haven.asp
- https://home.kpmg/xx/en/home.html
- Cover photo from Pexels
